|
3. Laser
A
special light source is used for recording holograms.
It is a laser. There are two main features, which
distinguish the laser light, and radiation of other
light sources. These are monochromatic radiation
and coherency. Monochromatic radiation is a radiation,
which spectrum is very narrow and it is visually
perceived as a pure color - red, green, etc. Coherency
is a more complicated concept. It is defined by
constancy of the wave-front phase in the space as
well as in the time. All the lasers are monochromatic
(to different extent), but coherency is inherent
in only such lasers, which are used for holography
or special measurements. We aren't going to consider
details of complicated theory of coherency, we can
say: the greater coherency of the laser radiation,
the greater depth of a scene is possible to be recorded
on a hologram. There are various types of lasers.
The following lasers are mostly involved in holography:
 Helium-Neon (He-Ne) laser Helium-Neon (He-Ne) laser
The main instrument of holographers. It is very
reliable, simple, economical and has good holographic
characteristics. LG-38, LGN-215, LGN-220 models
are widely used in Russia (see photo).
- Radiating wavelength is 633nm (red color).
- Radiating power: up to 60 mW.
- Coherency length: 15-20 cm.
Argon
laser
The powerful ionic laser radiating in blue&green
region of spectrum. It has great electric power
(5 - 10kW) and demands water-cooling. This laser
is irreplaceable for recording holograms of big
sizes.
- Main radiating wavelengths
514 nm (yellow and green color): 2-5 W,
488 nm (green color): 1-3 W
- Lines with small power
455 nm, 458 nm, 466 nm, 473 nm, 476 nm, 487 nm,
502 nm.
- Coherency length
Without Fabry-Perot interferometer: 5 cm
With Fabry-Perot interferometer: 2-3 m
Krypton
laser
The powerful ionic laser radiating in red region
of spectrum. It has great electric power (5- 10kW)
and demands water-cooling. This laser is irreplaceable
for recording holograms of big sizes.
- Radiating wavelength: 647 nm (red color).
- Radiating power: 1-3W
- Coherency length
Without Fabry-Perot interferometer: 5 cm
With Fabry-Perot interferometer: 2-3 m.
Cadmium
laser
Radiation in blue region of spectrum. It is suitable
for recording dichromate gelatin holograms and exposing
photoresist to record relief rainbow holograms.
- Radiating wavelength: 440 nm (violet and blue
color).
- Radiating power: up to 50mW
- Coherency length: 15 - 20 cm.
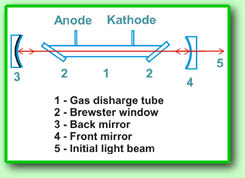 Let us consider construction
and basic principles of He-Ne laser, see fig. The
main element of the laser is gas discharge tube
1. This is a glass tube filled with helium
and neon mixture. When electric voltage is supplied
to the tube, the current passes through the gas
mixture and excites neon molecules. Neon molecules
transfer to the neutral state and emit red light
(it is well known for neon advertisement). Radiation
emitting along the tube is reflected back by mirrors
2 and 4 which form a resonator of
the laser. Radiation passes through the tube again.
The tube is filled with excited neon molecules and
the radiation intensifies. After several passes,
power of this radiation significantly exceeds power
of the initial radiation, so some part of the radiation
goes out through the front semitransparent mirror
of the resonator. Thus, generation of the coherent
radiation takes place. Coherency lasts out because
of multiply passes of the initial light beam through
the laser resonator. Due to a special construction
of output windows of the gas discharge tube (Brewster
windows) the polarized radiation is emitted by the
laser. Let us consider construction
and basic principles of He-Ne laser, see fig. The
main element of the laser is gas discharge tube
1. This is a glass tube filled with helium
and neon mixture. When electric voltage is supplied
to the tube, the current passes through the gas
mixture and excites neon molecules. Neon molecules
transfer to the neutral state and emit red light
(it is well known for neon advertisement). Radiation
emitting along the tube is reflected back by mirrors
2 and 4 which form a resonator of
the laser. Radiation passes through the tube again.
The tube is filled with excited neon molecules and
the radiation intensifies. After several passes,
power of this radiation significantly exceeds power
of the initial radiation, so some part of the radiation
goes out through the front semitransparent mirror
of the resonator. Thus, generation of the coherent
radiation takes place. Coherency lasts out because
of multiply passes of the initial light beam through
the laser resonator. Due to a special construction
of output windows of the gas discharge tube (Brewster
windows) the polarized radiation is emitted by the
laser.
References
1. Ishenko E. Ph., Klimkov Yu. M. "Optical
Quantum Generators", Sov. Radio, Moscow, 1968,
2. O. Svelto "Principles of Lasers", Plenum
Press, New York, 1989
-->
|